There are some instances where you have a large dataset but stored in different files, which you need to merge to conduct your analysis. This post demonstrates how to merge different data files into one file.
There are two ways of merging SPSS files: 1) by adding cases, or 2) by adding variables.
Merging files by adding cases
This option is used when the two or more files have the same variables but represent different cases.
An example is when you have the same survey conducted in different towns, different organisations, or different countries. The survey is the same but the observations are different and may therefore be stored in different files for each town, organisation, or country.
Before merging files by adding cases, it is important to ensure that the observations for each file have different identity number (ID number).
For instance, if the ID numbers for file 1 started from 1 to 100, the ID numbers for file 2 should not have these numbers. This is because each case should have a unique ID number. If the ID numbers are the same for each file, they should be changed.
To change the ID numbers in file 2, follow the following procedure:
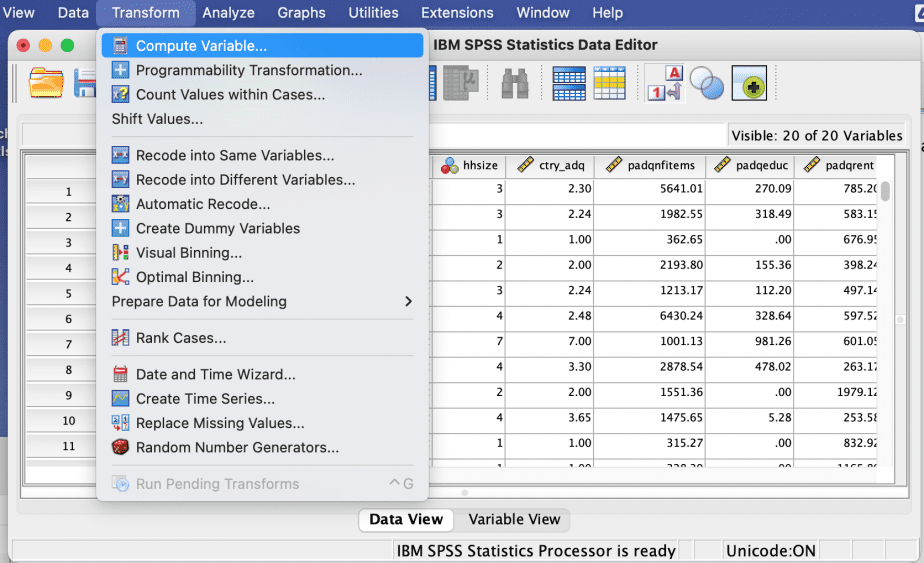
- Open the file, choose Transform menu > Compute variable.
- Type ID (or the variable name used for identity number) in the Target variable box, and then key in ID + 100 (or any number that is bigger than the number of cases in file 1) in the Numeric expression box. If file 1 has 100 cases and the ID number starts from 1 to 100, then file 2’s ID number will start from 101 if the above procedure is followed.
- Click OK > then OK in the dialogue box.
The above changes should be noted in the codebook for future reference.
The procedure is demonstrated in the images below:
Repeat the same procedure for the other files if the files to be merged are more than two.
To merge the files, follow the procedure below:
- Open file 1.
- Go to the Data menu > Merge files > add cases.
- From the dialogue box, select either “An open dataset” if file 2 is open. The file will be listed in the box. Alternatively select “An external SPSS data file” if file 2 is not open, and choose the file that you want to merge.
- Click continue > OK.
- Save the merged file using a different name using the “File > Save As” option. This ensures that the original files remain unchanged for future use.
The procedure is demonstrated in the images below:
Merging files by adding variables
This option is used if the different files have the same cases/observations but different variables.
For example, if file 1 has demographic variables only, file 2 has variables concerning household healthcare seeking practices and behaviour, file 3 has variables on household expenditures etc. You can merge these files to enable you perform different analyses using the different types of variables.
Before merging by adding variables, you must first sort the files using the procedure below:
- Sort the files using the ID variable in ascending order, that is, starting from the lowest to the highest value. Some datasets have more than one ID variable (for instance, a household survey dataset might have an ID for individuals in a household, and another ID for the households. In this case, you have to sort the data using both ID variables).
- To sort the data, go to Data menu > Sort cases.
- In the dialogue box that opens, click on the ID variable(s) and use the arrow to move it(them) to the “Sort by” box.
- From the “Sort order” option, select “Ascending” > then click OK.
The procedure is demonstrated below:
Once all the files have been sorted by ID variable(s), it is time to merge them. This is done using the procedure below:
- Go to Data menu > Merge files > Add variables.
- In the dialogue box, select either the option “An open dataset” if the file to be merged is open. If it is open, it will appear in the box below. If the file is not open, select the option “An external SPSS Statistics data file” and choose the file from its location. Then click continue.
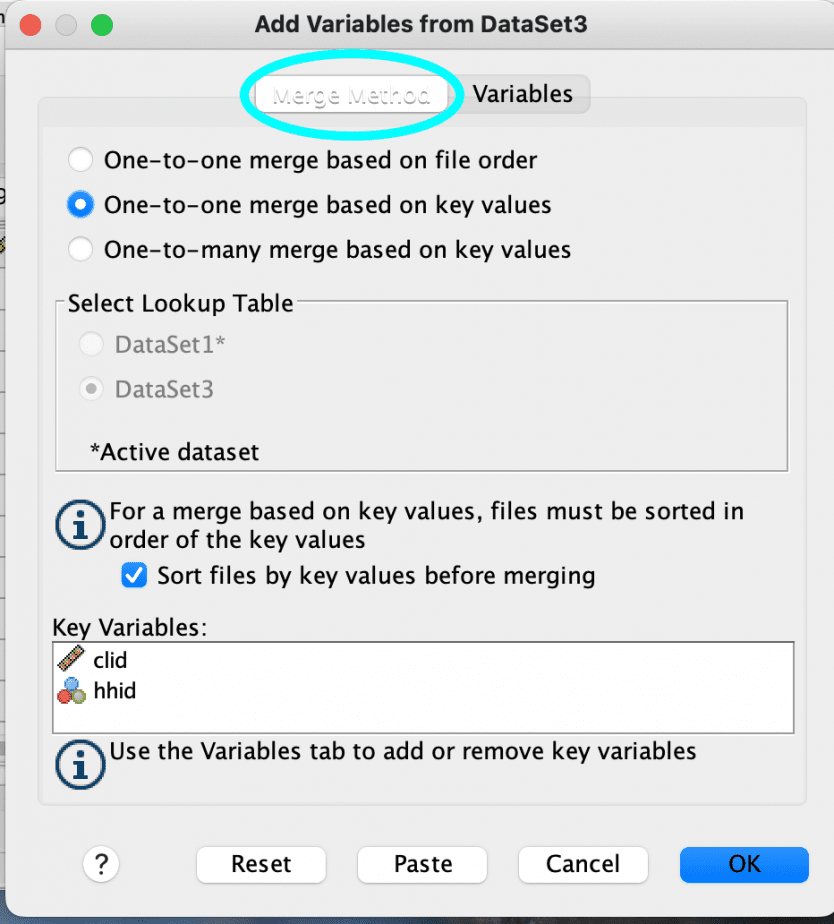
- A new dialogue box will open with two tabs: merge method and variables tabs.
- Click the “merge method” tab and choose the merge method to use. There are three options listed. The merge method will depend on the dataset you have in both files. One-to-one merge method is used to merge one case in file 1 with the same case in file 2; whereas one-to-many merge method is used to merge one case in file 1 with many cases in file 2.
- If you select the one-to-one merge based on key values or one-to-many merge based on key values, you will need to identify the key variables in the “key variables” box. The key variables are the ID variables that are used to merge the files.
- Click the “variables” tab. In the “Included variables” box, all the variables in both files will be listed. In the “Key variables” box, the ID variables will be listed.
- Click OK. The files will be merged.
- Save the merged file with a different name so that the original file remains unchanged.
The above procedure is demonstrated in the images below:
After merging, it is important to go through the merged file to ensure that the merging was done correctly and that the merged data makes sense.
In conclusion, merging files is necessary when you have separate data files with different cases or different variables that need to be merged to enable a more comprehensive data analysis. There are two ways of merging files in SPSS: merging by adding cases and merging by adding variables.
Related posts
How to Code a Questionnaire in SPSS (A Practical Guide)
SPSS Tutorial #1: Introduction to SPSS
SPSS Tutorial #2: Data Manipulation in SPSS