In this article, I discuss and demonstrate data modification in SPSS.
Data modification can take various forms. This article will cover: how to delete and add a case, how to delete and add a variable, how to move a variable, how to sort data, how to split data, how to select cases, and how to create variable sets in your dataset.
- How to delete a case in SPSS
- How to add a case in SPSS
- How to delete a variable in SPSS
- How to add a variable in SPSS
- Changing the position of a variable in SPSS
- Sorting data in SPSS
- Splitting data file in SPSS
- Selecting cases in SPSS
- Creating variable sets in SPSS
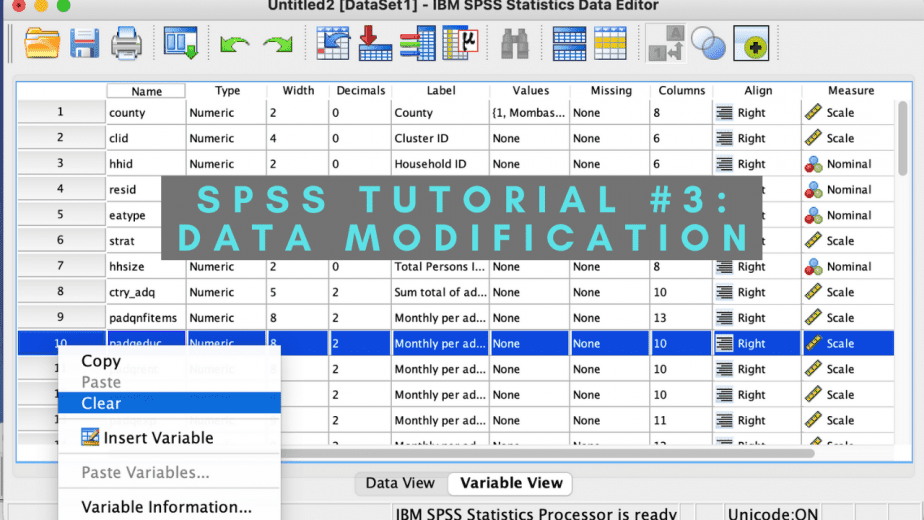
How to delete a case in SPSS
A case is the same as an observation.
Cases are the rows in the data view of the Data Editor.
To delete a case, go to the data view, then place your cursor on the first column with numbers, click on the number you want to delete to highlight the entire row of case, right click and select clear.
The case will be deleted from the dataset.
See the images below:
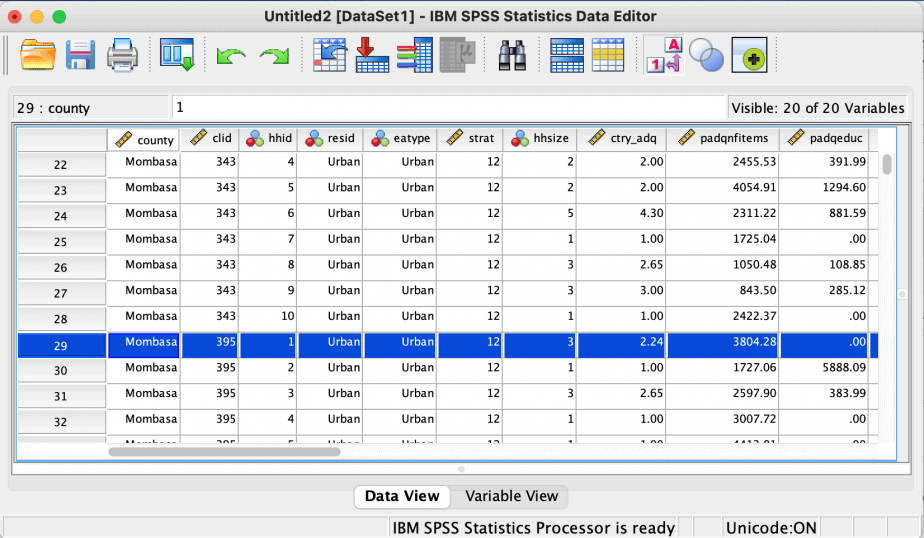
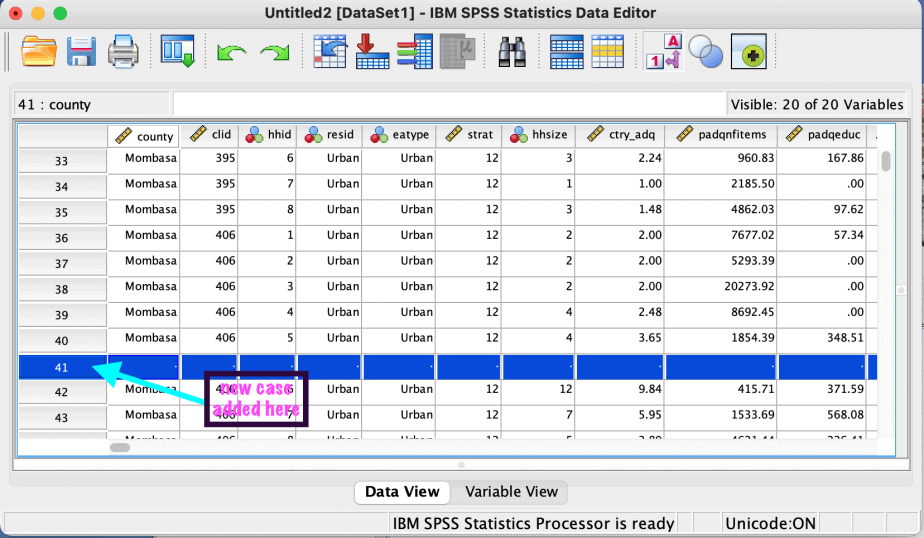
How to add a case in SPSS
If you want to add a case in between existing cases, click on the case below where you want the new case to appear and select that case. Then right click and choose add case. The new case will appear above the case you selected.
Example: I want to add a case between cases 40 and 41, I will highlight case number 41 then right click and choose add case. The new case will now be 41, and the old case 41 will now be case 42.
This is demonstrated in the images below:
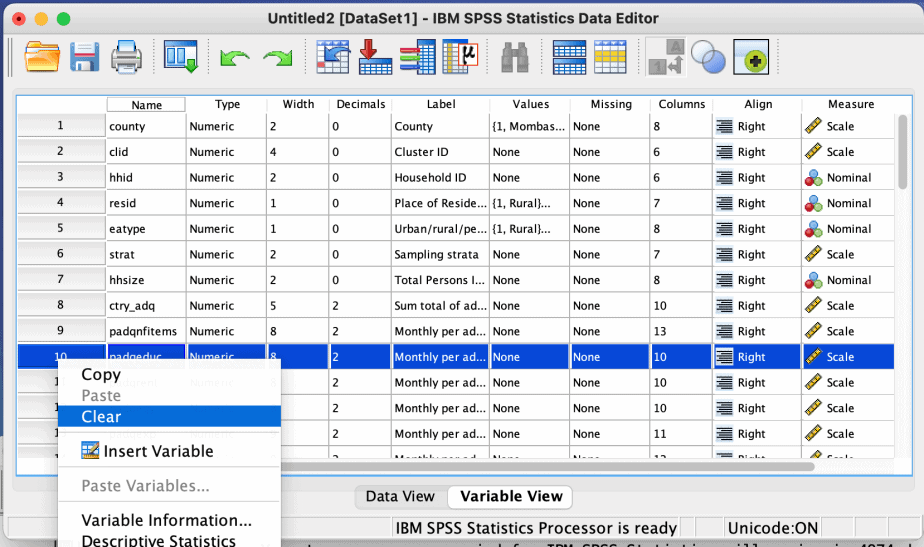
How to delete a variable in SPSS
There are two options: using the data view or the variable view.
Option 1: data view
To delete a variable, go to the data view in the Data Editor.
The variables are shown in the columns.
Go to the variable names and choose the variable you want to delete. Click on that variable name to select the entire variable.
Right click and select clear. The variable will be deleted.
Option 2: variable view
The second option is to use the variable view in the Data Editor.
Click on the variable you want to delete and select the entire row.
Right click and select clear. The variable will be deleted.
These two options are demonstrated below:
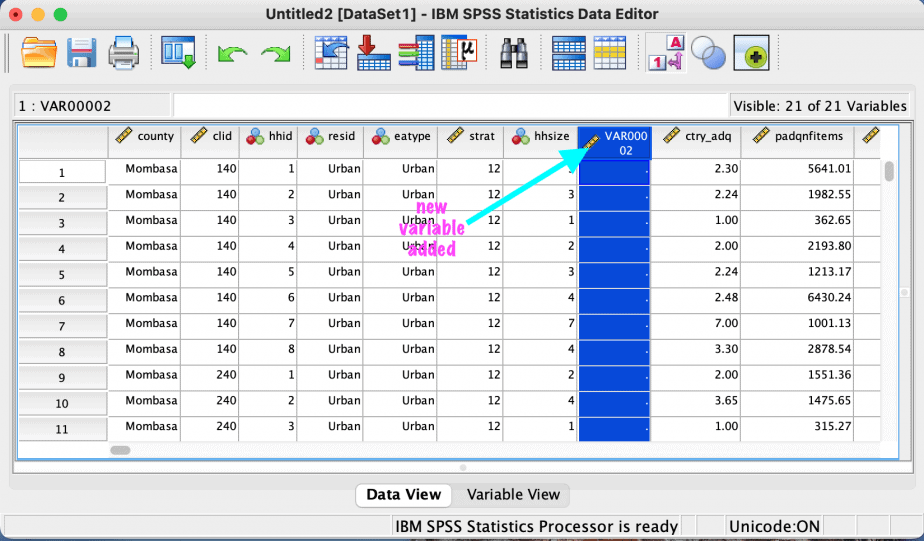
How to add a variable in SPSS
There are two options also: using the data view or the variable view.
Option 1: data view
To add a new variable between two variables, select the variable where you want the new variable to be.
Right click and choose insert variable.
The new variable will be added to the left of the selected variable.
Example: I want to add a new variable between the variables “hhsize” and “ctry_adq.” I will select the variable “ctry_adq”, right click and choose insert variable.
The new variable will be added to the left of “ctry_adq” as shown in the images below:
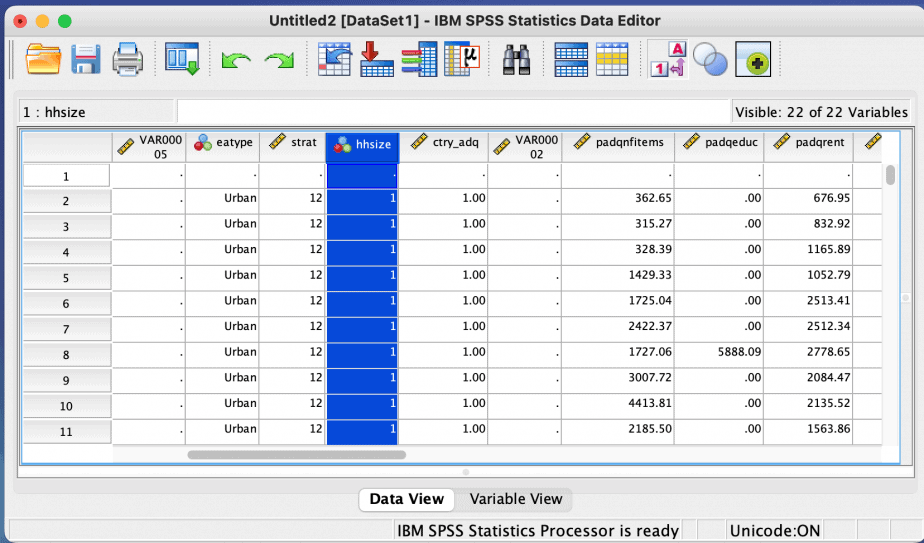
Option 2: variable view
Go to the variable view and select the variable where you want to insert the new variable.
Click on it and right click then choose insert variable.
The new variable will be inserted.
Example: I want to add a new variable between the variables “resid” and “eatype.” I will select “eatype” and right click then choose insert variable. The new variable will be inserted between “resid” and “eatype”, as shown in the images below:
Changing the position of a variable in SPSS
You may also be interested in moving a variable from its current location in the dataset to a different location.
Go to the variable view, click on the left-hand of the variable (the variable name) to highlight the entire row, hold down your left mouse button and drag the variable either up or down to where you want it to be.
As you drag it, a red line will show.
Once you reach the new desired position and the red line is showing, release the mouse button.
The variable will be placed in that new position.
Sorting data in SPSS
When creating a dataset, it is important to include an identifying variable, which helps to differentiate one case from another.
this identifying variable can take different forms depending on the sampling unit that was used. For instance, if the sample is for households, then you will have household ID as the identifying variable. On the other hand, if the sample is for individuals, then you will have individual ID etc.
The datasets are then arranged using the ID variable.
However, you may want to sort the data using a different variable, for example, age or household size etc.
To sort the data, go to the Data menu > sort cases.
From the dialogue box, select the variable that you want to use to sort your data, use the arrow to move it to the right pane (sort by section).
Select the sort order option desired (either ascending or descending) and click OK.
Your dataset will be sorted by household size starting from the cases with the smallest household size to the cases with the largest household size.
This is demonstrated in the images below:
To restore your dataset to the original state, repeat the same process using your identifying variable as the “sort by” variable.
Splitting data file in SPSS
In some cases, you may be interested in conducting the same analysis separately for different groups (e.g by sex: males vs. females).
To do this, you will need to split the data file into the various groups.
To split your data file:
Go to the Data menu > split file.
A dialogue box will open. Choose the option “compare groups” on the right hand side.
Then select the variable that you want to do the comparative analysis with. In this case, I selected “place of residence (urban vs. rural)”. Then click OK.
All the analyses you conduct after the file split will be based on the grouping variable you selected, which in this case will be place of residence groups (urban vs. rural).
If you want to restore the original settings, just click on the option “analyze all cases, do not create groups” and click reset. This will turn off the split file option.
See the images below:
Selecting cases in SPSS
In some cases, you may want to analyse certain cases only rather than all the cases in the datasets.
To do this, you will need to select only those cases and then conduct your analysis.
To select cases:
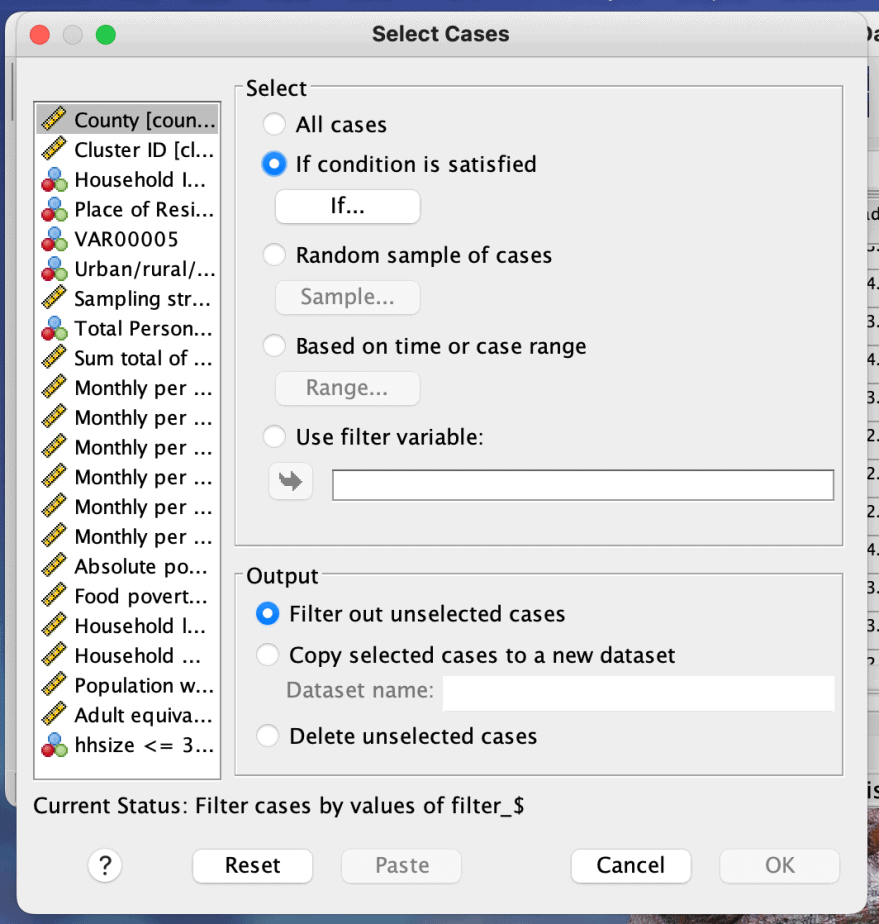
Go to Data menu > select cases.
A dialogue will open. Click on the “if condition is satisfied” option and click on the “if…” button.
This will open another dialogue box which is used to specify the condition.
In this example, I want to select cases with small household size (3 members and below).
In the select cases if dialogue box, I will select the variable “household size” and put the condition “hhsize <= 3” then click continue. Click OK on the select cases dialogue box.
SPSS will deselect all those cases with household size more than 3. This is shown in the data view where the cases with more than 3 household members are cancelled (left-most) column.
To turn off the select cases option, choose the “all cases” option in the select cases dialogue box, click reset then OK.
See the images below:
Creating variable sets in SPSS
This option is useful if you have a large dataset with many variables some of which you will not use.
You can create a sub-set of the data with only the variables that you intend to use for your analysis.
To create a set of variables from your dataset:
Go to the Utilities menu > Define Variables Sets.
A dialogue box will open.
In the “set name” box, type the name of your variables set.
Then select all the variables you want to include in your set and use the arrow to move them to the “variables in set” box.
Click “add set” then click close.
See the images below:
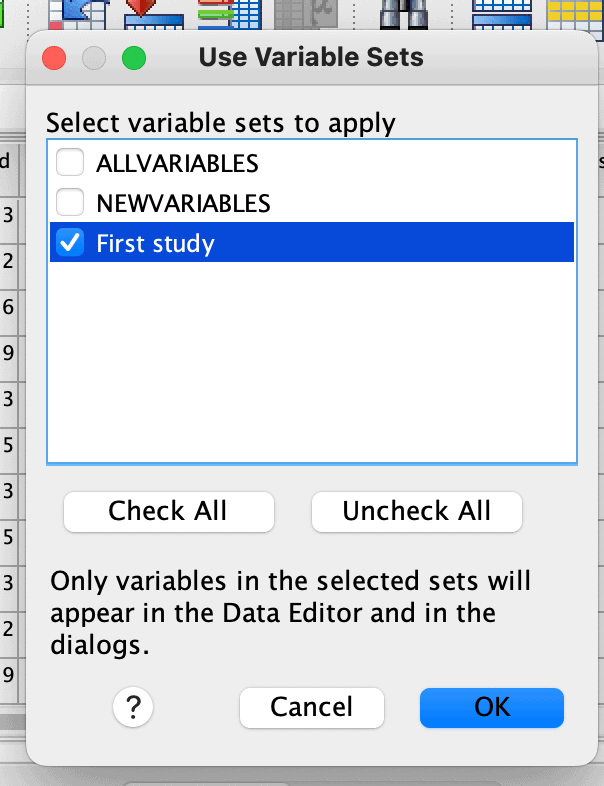
To use your variables set:
Go to Utilities menu > Use Variables Sets.
In the list of options, tick the variable set that you want to use and uncheck the rest, then click OK.
Your dataset will now only contain the variables that you specified in your set and this can be seen in the variable view of the Data Editor.
See the images below:
To turn off this option:
Go back to the Utilities menu > Use Variables Sets.
In the list of options, tick the “all variables” option, then click OK.
Your dataset will now contain all the original variables.
See the images below:
In conclusion, SPSS allows its users to make modifications to their datasets. There are many forms of data modifications that can be made as demonstrated in this post.
Related posts:
How to Code a Questionnaire in SPSS (A Practical Guide)
SPSS Tutorial #1: Introduction to SPSS